AI tools—and we don’t just mean trendy tools like ChatGPT—are evolving faster than ever and creating more opportunities to improve online learning.
While some of the AI tools you’ll see aren’t widely used in online learning yet (they’re mostly used by businesses) we’ll explain how they work and the ways they can be adapted for online learning.
1. Understanding emotion in different ways
Understanding emotions is complex because we all feel and express them in different ways. While emotion AI isn’t perfect, it can help instructors improve engagement and support learners where they need it most.
What is emotion AI?
Emotion AI, sometimes called affective computing, detects and interprets human emotions by analyzing text, voice (audio), and video and associating specific components with related emotions.
How can emotion AI be used in online learning?
Emotion AI technology can help learners with cognitive and/or physical disabilities communicate; detect signs of confusion and frustration; and pinpoint course activities that they are interested in or uninterested in.
What are the types of emotion AI?

Text Emotion AI
Analyzes written language to identify the sentiment and emotional tone of the content.
Example uses: analyzing written responses, like forum posts and course evaluations, to identify, understand, and address emotional states.

Voice Emotion AI
Example uses: monitoring learners’ spoken responses during online classes and virtual presentations to detect nuances in learner interest or distress.

Video Emotion AI
Observes body language, facial expressions, and gestures to determine emotional states.
Example uses: observing facial expressions and body language during video conversations and online exams to understand learners’ confusion and levels of interest or disinterest.
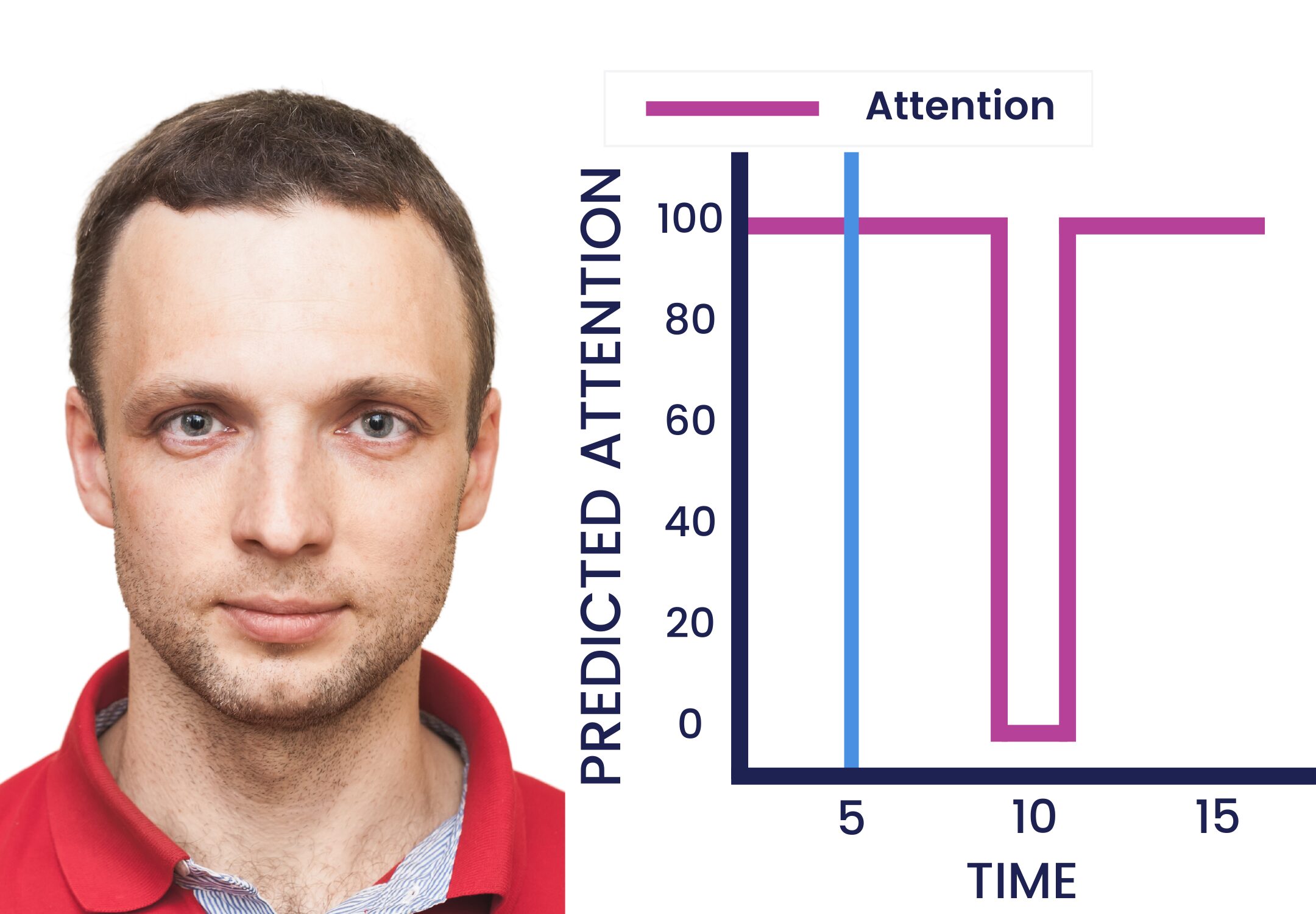
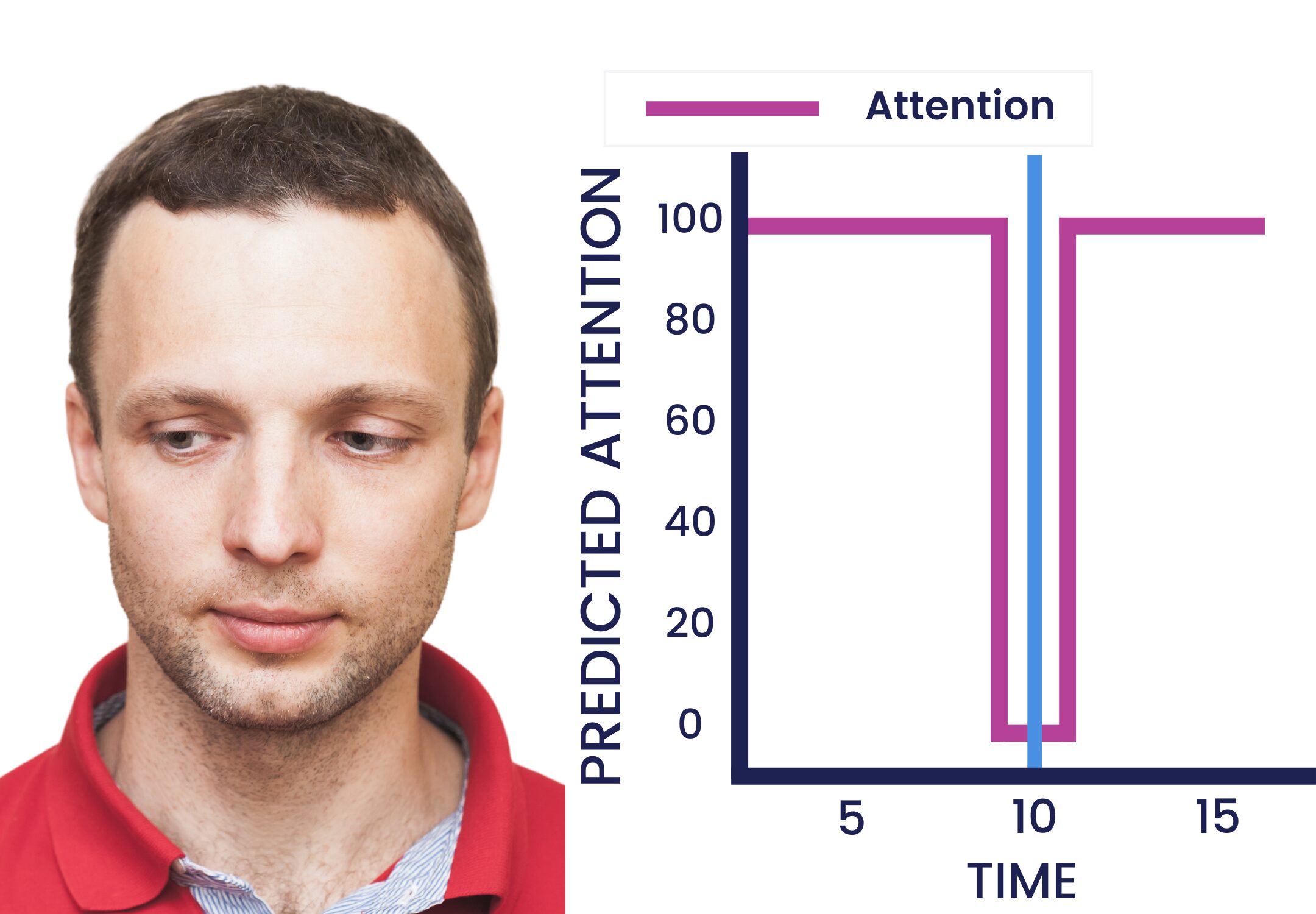
The images below illustrate how video emotion AI software might appear from an instructor’s perspective when reviewing, offering insights into learners’ interest and engagement.
“High Attention” highlights that learner attention increases when making eye contact.
“Low Attention” shows a decreased level of attention when they look away from the screen.
While eye contact with a webcam doesn’t necessarily mean they’re really paying attention, and looking away doesn’t mean they aren’t listening, when paired with other metrics, like how long they looked away, facial expressions, and other body language, it can help gain a broader understanding of behavior and emotion.
Educators can use these individual insights or similar data from all learners to understand certain activities that boost attention and engagement, which topics confuse learners, and more.
High Attention
Low Attention
High Attention
Low Attention
2. AI language tools that go beyond translations
Newer language-related AI can understand the nuances of languages like slang, accents, and dialects to build truly global dialogues in online courses.
Accent Recognition AI
Even if you’re a native English speaker, you’ve probably heard this or something similar from voice assistants. They’re about 95% accurate, sometimes more or less depending on which one you’re using, which is pretty good, right?
Sure, but that still means every 20th word is wrong, which is the exact length of the sentence you’re reading.
However, the accuracy varies depending on your accent… even if you’re a native English speaker.
Question
Answer
-
Which two U.S. accents are voice assistants more likely to understand?1. Southern
2. Midwest
3. Western
4. Eastern
-
1 & 3Southern and Western accents were understood more often than Eastern and Midwest accents.
Source: Washington Post, 2018 research
The research also found that people with non-native accents experienced 30% more inaccuracies when using voice assistants, with Spanish and Chinese accents being the least accurate. Imagine how frustrating that would be.
But there’s good news: accent recognition AI tools are available that are trained on extremely diverse data that allows it to better understand accents. They analyze and interpret speech patterns, intonations, and pronunciations specific to different accents.
Accent recognition AI can help improve the operability of voice-controlled technologies and generate more accurate live captioning and transcriptions.
Name Pronunciation AI
What’s an easy way to stifle a sense of inclusion and belonging? Mispronouncing someone’s name.
Even if it’s an innocent mistake, it’s probably something that person encounters daily. But there’s a solution that can help: name pronunciation AI.
How does name pronunciation AI work?
- Integrates throughout your online courses within the LMS, SIS, and other platforms to ensure that names are accurately pronounced.
- Uses databases of audio name pronunciations and algorithms that recommend correct pronunciations.
- Learners voice-record their names, and the recording is available throughout the platforms.
Name pronunciation AI can be used in:
- Online class discussions
- One-on-one advising sessions
- Virtual information sessions
- Recruitment conversations
- Student support
Realistic Sign Language Interpretation AI
Instead of using cartoon-like avatars, newer sign language interpretation AI creates a more realistic experience by splicing together videos of real people signing.
Some sign language AI can also provide real-time translation of spoken language and text to sign language and vice versa, making content accessible to deaf or hard-of-hearing learners.



3. Automatically finding leaked test content
Have you ever found your test questions leaked on the internet?
“Homework help” sites like Chegg and discussion forums like Reddit and Quora make it easy to find and share your test questions and answers.
You have 3 ways to tackle leaked test content:
1. Manually searching the internet on your own
You search the internet for individual test questions and send takedown requests if you find any.
2. Manually searching but with AI’s help
You select individual questions that the AI will search for and send your own takedown requests.
3. Automatically searching with AI
The AI does all the work by automatically searching the internet for all of your test content in a few minutes and giving you the ability to send one-click takedown requests.
- Search & Destroy™ automatically searches for all of your exam questions
- Search results show where any of your questions are leaked
- Send one-click takedown requests to sites displaying your questions
That’s it. No more leaked content concerns.
4. Large Language Models can help review college admissions essays without bias
Completely eliminating biases isn’t realistic, but they can and should be acknowledged and addressed, and AI can help, even though it can be biased too.
How can AI be biased?
AI reflects the biases of the people using it, the data it’s trained on, and the ways it’s used.
For example, if AI is trained on biased data, such as data from underrepresented groups, there’s a ripple effect that can impact algorithms, outputs, and future models.
The good news is that AI biases, similar to human biases, can be recognized and addressed to help reduce them.
Which would you pick?
If you were in charge of admissions—and let’s pretend time constraints don’t exist—would you:
- Only review objective data, like standardized test scores and GPAs
- Review objective data and understand other areas of who they are, like their personal qualities
Generally speaking, most would choose to consider personal qualities like personality, character, leadership, and life experiences.
While personal qualities are more subjective than test scores, research shows that they can predict success in school and life. Reviewing these qualities takes more time than reviewing objective information, like test scores and GPAs. But Large Language Models can help.
Large Langage Models (LLM)
What are large language models?
Large Language Models are a type of AI that can understand, interpret, and generate human language by analyzing and learning from extensive datasets.
How do LLMs work?
LLMs are trained by “reading” billions of pieces of text from various sources, like internet articles and forums, scientific research, textbooks, newspapers and magazines, and more.
This training helps them learn patterns and understand how words and sentences are formed in different formats and contexts.
LLMs don’t actually understand language, they’re just really good at predicting what word should come next. The two models we’ll discuss are unidirectional and bidirectional
- Unidirectional: predicts the next word based on previous words
- Bidirectional: analyzes text from both directions to predict a word in context
RoBERTa vs. ChatGPT
Both are LLMs that share the same architecture but excel in specific tasks, similar to cars with the same frame but different tires and suspension systems for certain terrains.
- RoBERTa (bidirectional) drives better in the city (understanding language nuances and context), but it can still make it on certain off-road trails (creating content).
- GPT (unidirectional) drives best on off-road trails, but can navigate some city streets.
The University of Pennsylvania used a LLM, RoBERTa to review college admissions essays for personal qualities
Research published in October 2023 by the University of Pennsylvania indicates that certain LLMs, if trained properly and thoroughly, can review admissions essays for personal qualities that predict college graduation on par with human admissions staff.
The researchers and their team analyzed over 300,000 college essays and scored them on the absence or presence of seven traits: prosocial purpose (helping others), leadership, learning, goal pursuit, intrinsic motivation, teamwork, and perseverance.
Then they trained RoBERTa to recognize and evaluate similar qualities and characteristics in essay submissions without showing biases toward race, gender, or socioeconomic status. RoBERTa was used because it excels at understanding the context and meaning of language, which makes it an effective tool for understanding emotions, text classification, and translations.
Research results and takeaways
RoBERTa recognized personal qualities without bias
It recognized qualities like teamwork and intrinsic motivation in applicants from diverse backgrounds, without showing bias towards race, gender, or socioeconomic status.
RoBERTa’s predictions were accurate
Its predictions of the likelihood of students graduating were slightly more accurate than humans, but not by much.
The researchers recommend using AI with optimism and caution
“An AI approach to measuring personal qualities warrants both optimism and caution… We recommend AI be used to augment, not replace, human judgment. No algorithm can decide what the goals of a university’s admissions process should be or what personal qualities matter most for that community.”
5. Preventing remote access software contract cheating
Have you ever had a support technician take over your desktop and fix your computer from a remote location?
That’s basically how remote access software is used to cheat on exams.
A person pays a test-taking service to have one of their experts control their computer and take the exam from a remote location.
Even though the person getting credit appears to be sitting in front of the camera during the test, it’s the off-camera expert who is actually answering the questions.
And since the person getting credit stays on screen during the exam, ID verification methods won’t help.
How can you stop remote access cheating?
Honorlock’s remote proctoring platform has a few ways to help:
- Recording the desktop and requiring specific keyboard commands immediately before starting the exam: Exam admins use Honorlock’s exam settings or test rules to require test takers to use keyboard commands, such as Ctrl+Alt+Del (Windows) or Cmd+Opt+Esc (Mac), to display the applications and processes running on the device.
- Displaying countries: Honorlock’s Analytics Hub™ shows the countries that tests were taken in based on IP address. If any tests are taken in countries with no known test takers, it may indicate the use of remote access test-taking services.
- Blocking applications: Honorlock’s proctoring platform gives exam administrators the ability to block specific applications that can be used for remote access.
6. Using AI for on-demand tutoring
Whether intentionally built for tutoring or adapted, AI tools such as intelligent tutoring systems, chatbots, and writing assistants offer 24/7 interactive tutoring and support, which enhances learning while building a more diverse and inclusive educational environment that accommodates various learning styles and needs.
They also offer real-time feedback, which is crucial for learners with intellectual disabilities because it helps them make connections between their work and the instructor’s feedback.
Intelligent Tutoring Systems (ITS)
Intelligent Tutoring Systems simulate one-on-one human tutoring, offering tailored feedback and adapting course materials to meet each learner’s needs.
They can guide learners through problem-solving steps, offer hints, break down complex topics, and recommend additional relevant content.
While an ITS can benefit any subject, it’s particularly beneficial for subjects like math, which require—for the most part—a lot of repetition.
Here’s how an ITS could work for an algebra course:
- The ITS assesses the learner’s understanding of basic algebraic concepts and their ability to solve problems.
- After assessing knowledge, it customizes learning activities and offers additional content based on their needs.
- If the learner struggles in a specific area, it provides extra help, like step-by-step explanations and practice problems.
- If the learner excels in a topic, the ITS gradually progresses to more advanced concepts and activities.
- The ITS provides immediate feedback and additional context, allowing learners to recognize errors and learn to correct them.
Chatbots
ChatGPT, Google Bard, and other chatbots can provide learners with instant tutoring and support anytime they need it.
Learners can use chatbots to dig deeper into complex subjects, brainstorm ideas, provide feedback on written work, translate text, and check writing quality.
AI writing assistants
Writing tools like Grammarly and Quillbot have been around for a few years now, but they’re evolving.
Initially, they just helped improve writing by correcting grammar, spelling, and style issues.
But now, they’re incorporating AI that can instantly make writing more concise, easier to understand, or sound a specific way, such as being more assertive.
These tools are particularly useful for individuals writing in a second language and for those with learning disabilities, as they can boost confidence and deliver different forms of corrections and feedback immediately.
Regardless of which AI tools you use, make sure that they’re used purposefully, ethically, and with full transparency. Always keep in mind that AI tools are just that—tools. They aren’t a replacement for the people using them.